Genetic Councelling

The Key Role of Genetic Counselling in Safeguarding Family Health and Future Generations
Genetic counselling serves as an effective tool in managing and preventing hereditary diseases, playing a crucial role in safeguarding the health of families and future generations. This process empowers individuals and families to make informed decisions regarding their health and the health of their children by gaining a clear understanding of genetic and hereditary risks.
In genetic counselling, specialists utilise scientific knowledge and meticulous analysis of family histories and genetic sequences to identify the risk of specific diseases. This information helps parents make more informed choices about their reproductive options, lifestyle practices, and other health-related decisions.
Furthermore, genetic counselling can aid in preventing the transmission of genetic disorders to future generations. By identifying and managing these risks, families can work towards maintaining their health and the well-being of their children, ultimately improving their quality of life. This not only impacts the individual but also contributes positively to the broader community, fostering a healthier future for all.
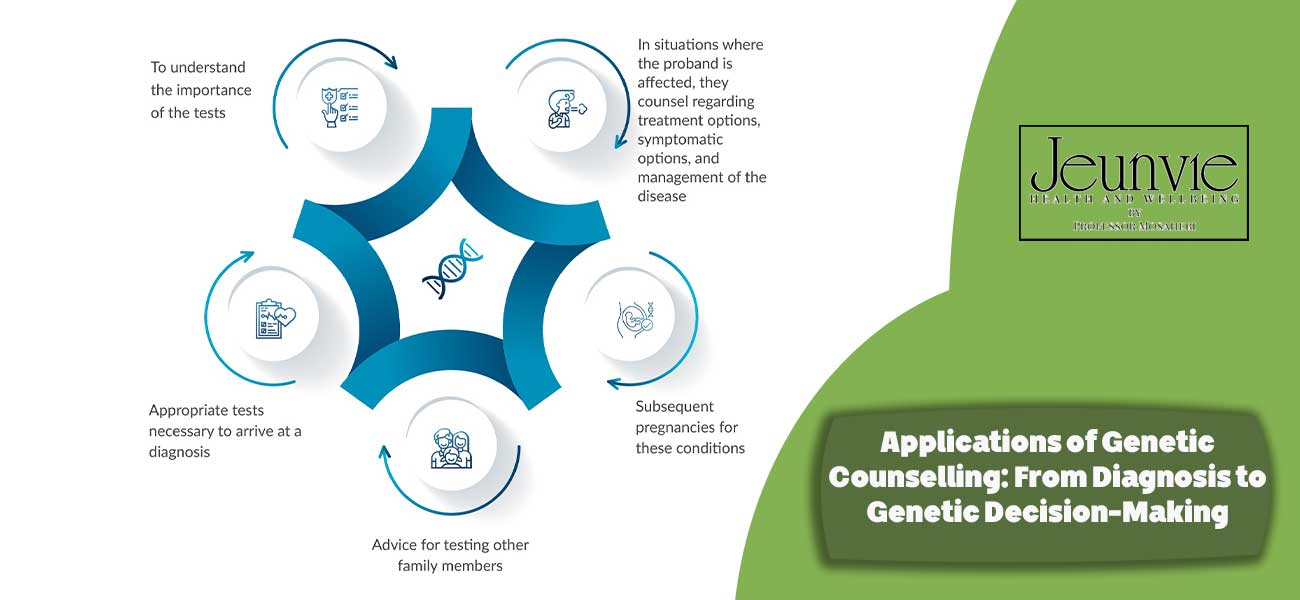
Applications of Genetic Counselling: From Diagnosis to Genetic Decision-Making
Genetic counselling, a specialised field within medical science, plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and management of hereditary diseases. This process involves the assessment, diagnosis, and provision of strategies to mitigate genetic risks, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for individuals and families.
1. Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders
One of the primary applications of genetic counselling is the diagnosis of genetic disorders. Genetic counsellors can identify patterns of inheritance by analysing family pedigrees and medical histories. In many cases, these diagnoses can lead to the early detection of conditions such as cystic fibrosis, haemophilia, and rare metabolic diseases. Early diagnosis empowers individuals to better plan for their disease management.
2. Management of Hereditary Diseases
Once a condition has been identified, genetic counselling can assist individuals and families in gaining a comprehensive understanding of their hereditary disease, thereby enabling them to make more informed decisions about its management. Genetic counsellors can provide information on treatment options, lifestyle modifications, and medical needs. This information empowers individuals to take an active role in their disease management.
3. Future Planning
Genetic counselling also empowers parents and families to plan for the future. If a genetic condition exists within a family, genetic counsellors can assist parents in making informed decisions about pregnancy, reproductive choices, and methods of preventing the transmission of hereditary diseases to future generations. These decisions may include options such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF) with preimplantation genetic diagnosis or counselling on adoption.
4. Education and Awareness
Moreover, genetic counselling helps individuals and families develop a greater understanding of their genetic conditions and associated risks. This education can empower individuals to make more informed health decisions and improve their understanding of their health and the health of future generations.
5. Psychological Support
Genetic counselling can also serve as a source of support for individuals at risk of hereditary diseases. The emotions and concerns associated with genetic issues can significantly impact an individual’s psychological well-being. Genetic counsellors can provide counselling and information to help individuals cope with these challenges.
In conclusion, genetic counselling is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of hereditary diseases. It empowers individuals and families to make informed decisions and improve their quality of life.

What is Genetic Counselling and Why is it Important?
Genetic counselling is a specialised process that provides individuals and families with information about genetic conditions and associated risks. It is typically conducted by qualified genetic counsellors who possess expertise in diagnosing and managing inherited disorders.
Definition of Genetic Counselling: Genetic guidance involves the assessment and analysis of an individual’s genetic and family history. This process includes the examination of family pedigrees, medical history, and genetic testing. The primary aim of genetic counselling is to identify genetic risks and provide sufficient information to support informed health and family decisions.
Importance of Genetic Counselling: Genetic counselling holds significance for several reasons:
- Early Diagnosis: This process can facilitate the early identification of genetic conditions, leading to improved management and treatment options.
- Risk Awareness: Genetic counselling helps individuals and families understand their genetic risks and make more informed decisions regarding their health and the health of future generations.
- Future Planning: With knowledge of genetic conditions, families can make informed decisions about pregnancy, reproductive choices, and methods to prevent the transmission of hereditary diseases to future generations.
- Emotional Support: Genetic counselling also provides emotional support, assisting individuals in coping with the emotions and concerns associated with genetic issues.
In conclusion, genetic counselling not only furnishes essential information for making informed health decisions but also empowers individuals and families to enhance their quality of life and prevent genetic disorders.
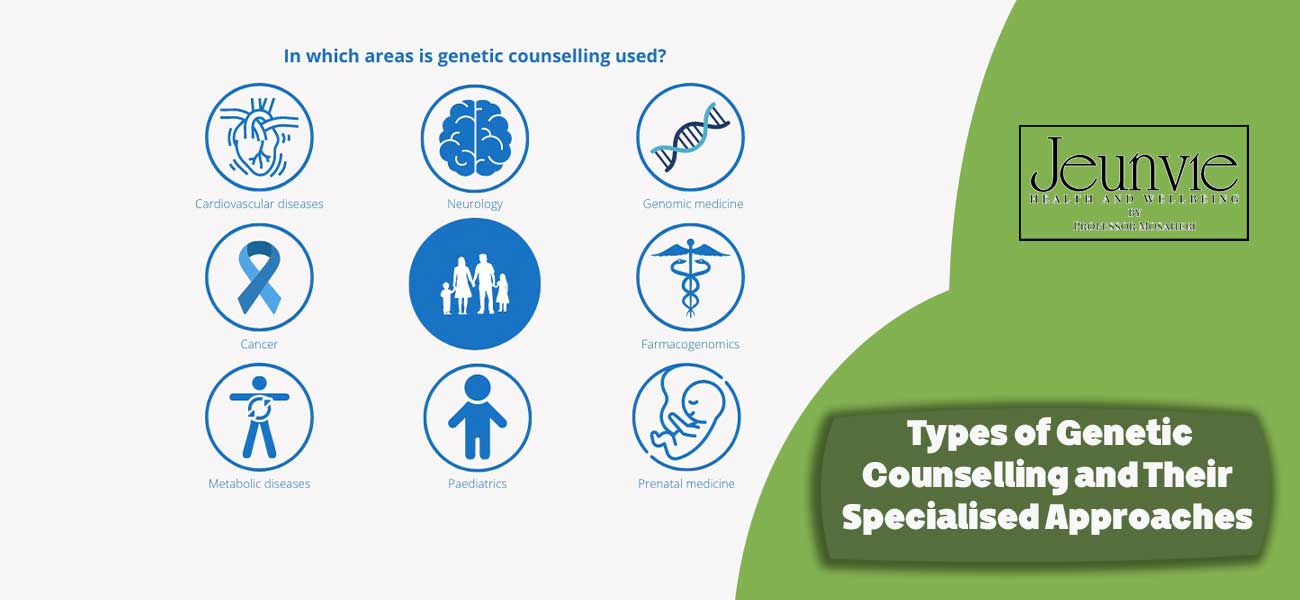
Types of Genetic Counselling and Their Specialised Approaches
Genetic counselling, as a specialised field, encompasses various types, each addressing specific needs and circumstances. This section introduces the different types of Genetic guidance and their specialised approaches:
Paediatric Genetic Counselling
This type of counselling focuses on identifying and managing genetic conditions in children. Paediatric genetic counsellors can identify conditions such as cystic fibrosis and other inherited disorders by assessing family history and conducting genetic tests. The aim of this counselling is to provide strategies for the timely management and treatment of childhood diseases, preserving the health of future generations.
Reproductive Genetic Counselling
This type of counselling assists parents who are experiencing fertility problems or have concerns about passing on genetic conditions to their offspring. Genetic counsellors can provide information on methods such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF) with preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). The goal of this counselling is to help couples make informed decisions regarding pregnancy and to select appropriate methods to prevent the transmission of diseases.
Adult Genetic Counselling
This counselling supports adults who are at risk of developing inherited disorders. Counsellors in this area can examine family history, identify patterns of inheritance, and provide information about conditions such as hereditary cancers and heart diseases. This type of counselling assists individuals in taking preventive measures and making suitable plans for managing their health.
Neurogenetic Counselling
This type of counselling focuses on inherited neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetic counsellors can identify genetic risks associated with these diseases and provide information on management and treatment. This counselling helps individuals and families cope with the psychological and social challenges linked to these conditions.
The various types of Genetic guidance empower individuals and families to receive tailored information and support based on their specific needs. This process not only contributes to the prevention and management of genetic diseases but also enhances the quality of life for individuals and families.

Paediatric Genetics: The Role of Counselling in Safeguarding Future Generations
Genetic counselling services in the field of paediatric genetics serve as a vital tool for identifying and preventing genetic disorders in children. This type of counselling assists parents and families in gaining a better understanding of the genetic risks that may impact their offspring, enabling them to take proactive measures to safeguard the health of future generations.
The Importance of Genetic Counselling in Identifying Genetic Disorders:
Genetic counsellors analyse family medical histories and conduct genetic tests to identify hereditary conditions such as cystic fibrosis, metabolic disorders, and other genetic anomalies. Early identification not only facilitates timely treatment but also provides the opportunity for planning and managing diseases in their initial stages.
Disease Prevention:
Genetic guidance empowers parents to make informed decisions about pregnancy and the upbringing of their children, based on their awareness of genetic risks. For instance, if there is a history of genetic disorders within the family, counsellors can offer preventive options, such as preconception testing or the selection of assisted reproductive technologies.
Safeguarding Future Generations:
With the information acquired from specialised Genetic guidance, families can actively engage in processes aimed at preventing genetic disorders, and by fostering necessary awareness, they can contribute to the enhancement of the health of future generations. Ultimately, specialised Genetic guidance is not only effective in identifying diseases but also plays a crucial role in preserving the health and quality of life for children and future generations.

Cancer Genetics: Guidance for the Prevention and Early Detection of Hereditary Cancers
Cancer genetic counselling is an essential tool for identifying and preventing hereditary cancers. As some cancers can be inherited within families, guidance in this area helps individuals and families better understand their risks and take proactive steps to prevent and detect these diseases early.
Identifying Genetic Risks
A key aspect of cancer genetic counselling is identifying inherited patterns that may increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. By reviewing family medical histories and conducting genetic tests, genetic counsellors can ascertain if family members are at risk for cancers such as breast, ovarian, prostate, and colorectal cancer.
Cancer Prevention
Once risks are identified, genetic counselling empowers individuals to make more informed decisions regarding cancer prevention. For example, if an individual or family is found to have specific genetic mutations that heighten their cancer risk, they can explore preventive options such as prophylactic surgery, regular screening, and lifestyle modifications.
Early Detection
In addition to prevention, genetic counselling plays a crucial role in the early detection of cancer. Individuals at risk can be monitored more closely and diagnosed earlier through regular screening. This can lead to timely treatment and improved outcomes.
Emotional Support and Guidance
Cancer genetic counselling can also serve as a source of emotional support for individuals and families. Understanding risks and coping with cancer-related concerns can be emotionally challenging, and counsellors can assist individuals in navigating these challenges.
Ultimately, cancer genetic counselling not only aids in identifying and preventing hereditary cancers but also equips individuals and families with the tools to make informed decisions about their health and the health of future generations. This process can enhance quality of life and contribute to a healthier population.

Early Diagnosis and the Importance of Initial Processes in Genetic Counselling
Early diagnosis of genetic diseases plays a crucial role in managing the health of individuals and families. Genetic counselling assists individuals and families in identifying inherited diseases at an early stage, allowing them to plan and take preventative measures to improve their quality of life.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
The early identification of genetic diseases enables individuals to take necessary actions before symptoms manifest. This includes preventive treatments, lifestyle modifications, and closer health monitoring.
Initial Processes in Genetic Counselling
The initial processes in genetic counselling encompass the following:
- Medical History: Gathering information about an individual’s family and medical history.
- Genetic Testing: Conducting genetic tests to identify mutations and inherited conditions.
- Analysis and Counselling: Providing an analysis of test results and counselling individuals and families on available options.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
- Better Disease Management: Individuals can commence appropriate treatments earlier.
- Awareness and Education: Families can make more informed decisions about pregnancy and childcare with knowledge of genetic risks.
- Preventing Disease Transmission: Early identification can help prevent the transmission of diseases to future generations.
Table: Initial Processes in Genetic Counselling
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Reviewing medical and family history to identify inheritance patterns. |
| Genetic Testing | Conducting necessary tests to identify genetic mutations. |
| Analysis of Results | Analysing the obtained data and assessing risks. |
| Counselling and Guidance | Providing appropriate information and advice to individuals and families. |
| Management Planning | Assisting in planning for disease management and treatment options. |
In conclusion, early diagnosis and the initial processes of genetic counselling empower individuals and families to enhance their health and that of future generations through increased knowledge.

Reproductive Genetics: How Genetic Counselling Aids Fertility Decisions
The Role of Genetic Counselling in Reproductive Processes
Genetic counselling for reproduction assists parents and couples who are planning to start a family in understanding the genetic risks associated with their offspring. This form of guidance is particularly important for those with a family history of genetic conditions or who possess genetic conditions themselves.
Identifying Genetic Risks
Genetic counsellors can identify potential genetic risks by reviewing a couple’s medical and family history. This process may involve genetic testing to detect mutations and inherited disorders. Awareness of these risks empowers couples to make informed decisions regarding pregnancy and fertility treatments.
Prevention Methods
Genetic counselling can help couples select appropriate options to prevent the transmission of genetic conditions to future generations. For instance, if a couple is found to be at high risk of passing on a specific genetic disorder, counsellors may suggest methods such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF) combined with preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). These methods enable couples to avoid the birth of a child with a genetic disorder.
Knowledge and Decision-Making
By providing accurate and clear information, genetic counselling empowers couples to make informed decisions about their fertility. This information not only helps them comprehend the associated risks but also assures them that they can choose prevention and treatment options based on their specific circumstances.
Ultimately, genetic guidance in reproduction plays a pivotal role in supporting couples in making informed healthcare decisions. This process not only assists in identifying and preventing genetic disorders but also contributes to the health and well-being of future generations.

Neurogenetics: Diagnosing and Managing Inherited Neurological Disorders through Genetic Counselling
Genetic counselling in neurology plays a pivotal role in identifying and managing inherited neurological disorders. This specialised counselling empowers individuals and families to understand their genetic risks, access appropriate treatment options, and make informed decisions regarding their healthcare.
Diagnosing Inherited Neurological Disorders
Inherited neurological disorders are conditions that can be passed down through families. Genetic counsellors can ascertain the inheritance patterns of these disorders by reviewing family medical histories and conducting genetic tests. Examples of such disorders include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Management and Treatment
Once an inherited neurological disorder has been diagnosed, genetic guidance can assist patients and their families in developing effective management plans. This may involve providing information about treatment options, medical care, and emotional support. Counsellors can also help families navigate the psychological and social challenges associated with neurological conditions.
Prevention and Future Planning
Armed with the information gained from genetic guidance, families can make more informed decisions regarding pregnancy and child care. This knowledge enables them to identify genetic risks and implement preventive measures when necessary.
In conclusion, genetic guidance in neurology not only assists in diagnosing and managing inherited neurological disorders but also enhances the quality of life for individuals and families. By providing information, support, and guidance, genetic counsellors empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare and navigate the challenges associated with these conditions.

Advanced Genetic Issues: New Challenges and Opportunities in Genetic Counselling
Genetic counselling has become an indispensable tool for understanding and managing genetic diseases and related conditions. With advancements in science and technology, new challenges have emerged in this field that require careful consideration and management. This text will explore the new challenges and opportunities in genetic guidance.
Challenges in Genetic Counselling
- Genetic Complexity: As our understanding of genetics deepens, the complexities of how genes influence diseases have become more apparent. Many genetic disorders are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, making them challenging to identify.
- Public Awareness: A lack of awareness about genetic counselling and its benefits can deter individuals from seeking assistance. This is particularly evident in communities with lower levels of education.
- Ethical and Social Issues: Ethical questions surrounding genetic testing, such as the privacy of genetic information and reproductive choices, pose significant challenges for genetic counsellors.
Opportunities in Genetic Counselling
- Technological Advancements: Novel technologies, such as whole genome sequencing, provide greater opportunities to identify genetic disorders and predict risks.
- Increased Awareness: As public awareness and access to information increase, more individuals are seeking genetic guidance, leading to improved quality of life.
- Disease Management: genetic guidance can serve as a tool for managing diseases and preventing the transmission of disorders to future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, genetic guidance plays a vital role in addressing both the challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving field of genetics. This process empowers individuals and families to gain a deeper understanding of genetic issues and make informed decisions about their health and the health of future generations. Given the rapid advancements in genetics, the importance of specialised genetic guidance will continue to grow and require ongoing development.
Reviews
Contact
- Our Clinic : 4th Floor, 93-95 Wardour Street W1F 0UD
- phone: 07843 055357
- email:info@jeunviewellbeing.health
- Copyright 2025 Jeunvie Health and Wellbeing
